Program Learning Outcomes
Program Learning Outcomes
PURPOSE
The purpose of learning outcomes is to ensure that students are equitably achieving learning goals. Outcomes assessment helps faculty to identify specific improvements that need to be made to curriculum and pedagogy. Learning outcomes is also one of the tools faculty and administration use to make informed decisions that meet the needs of our students, disciplines, and community.
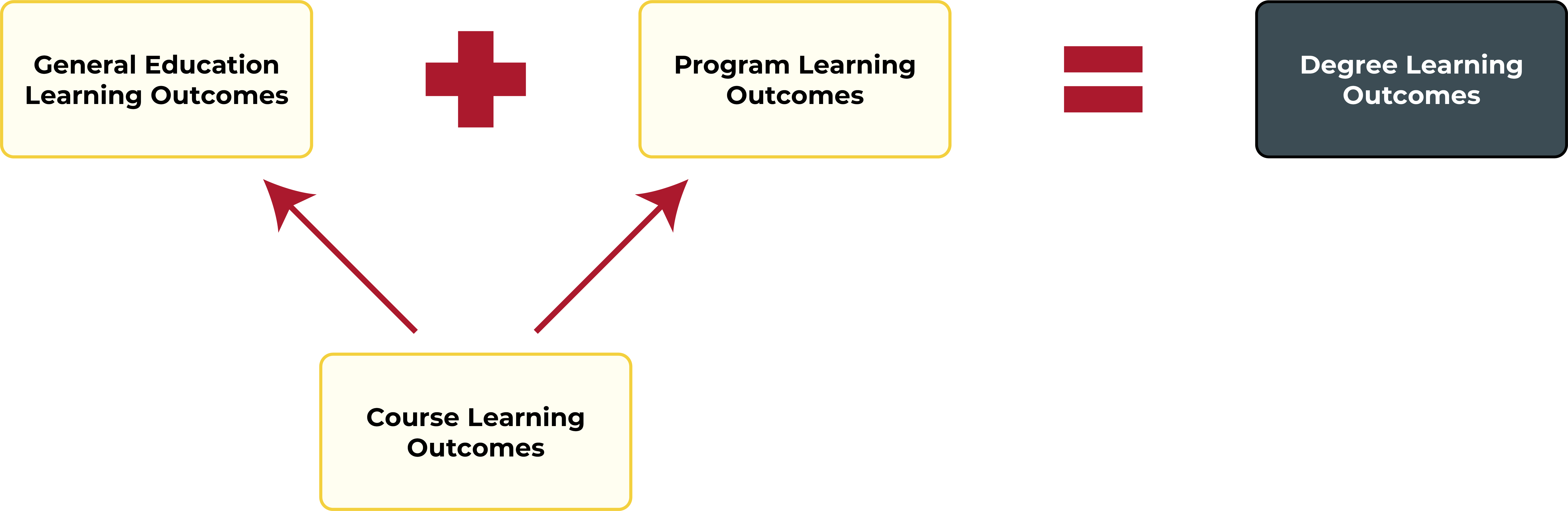
LIST OF OUTCOMES AND COURSE MAPPING
At Skagit Valley College, each learning outcome is mapped to one or more specific courses within or across programs. Those outcomes can be general education (GELO), program (PLO), and/or course-specific learning outcomes (CSLOs). Note: CSLOS are not yet loaded in Canvas.
| Academic Area | Outcomes List | Outcomes & Courses Mapping |
| General Education | View List | View Mapping List |
| Transfer Programs | View List | View Mapping List |
| Professional Technical Programs | View List | View Mapping List |
Course Specific Learning Outcomes
CSLOs Course Outline
Faculty are expected to assess learning outcomes that are mapped to courses they are teaching during a current quarter. They will also continue to assess those outcomes throughout the year the outcomes are scheduled to be assessed.
Current Program Review Cycle
- Year 1: Summer 2024 through Spring 2025
- Year 2: Summer 2025 through Spring 2026
- Year 3: Summer 2026 through Spring 2027
- Year 4: 2027-28 Review and Analyze Cumulative Data
Previous Program Review Cycle
- Year 1: Summer 2019 through Spring 2020
- Year 2: Summer 2020 through Spring 2021
- Year 3: Summer 2021 through Spring 2022
- Year 4: 2022-23 Review and Analyze Cumulative Data
2019-2023 Individual Program Review Results
Note 1: Instructors are encouraged to continue to assess learning outcomes applicable to their courses even before or beyond the year the outcome is scheduled to be assessed. The more often faculty can assess an outcome within in a course and between quarters, the better.
Note 2 : Course-specific learning outcomes are not yet loaded in Canvas. If you need help, contact the eLearning Team at elearning@skagit.edu.